In previous versions of Solaris we have used the ifconfig command and configuration files within /etc to manage the network configuration. Now we have new kids on the block in the shape of dladm and ipadm. In this tutorial we see how we can configure the network using these tools
Network Profiles
On a newly installed Solaris 11 machine we will have network profiles
- Automatic
- DefaultFixed
We can also add are own profiles and we will see that in a later lesson. Additonally we have three locations
- Automatic
- NoNet
Again we can add to these if we need. These locations and profiles store the network configuration and can be listed from the command line with
netcfg list
These represent the new storage of IP Configuration in Solaris 11. We can use the command ipadm(/usr/sbin/ipadm) and dladm(/usr/sbin/dladm) to manage the address information with the profiles.
dladm
The data-link adm tool can be used to manage the layer 2 element of networking on solaris, so the interfaces and bridging ports etc.
dlmadm help
Will show the sub-commands available to you:
 ;
;
To see the physical NICS that we have in Solaris 11 we can use the command
dladm show-phys
We can see from the output that the default name for the first card is net0.
ipadm
To disable an interface or bring its sate to down we could use the command
ipadm delete-ip net0
and
ipadm create-ip net0
The create-ip sub-command will create the IP Interface again.
To add ip addresses to the IP Interface the subcommand create-addr can be used
ipadm create-addr -T dhcp net0
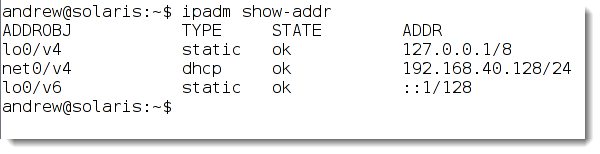
If we do not add an alias after net0 (which is the interface name ) then v4 will be used. If that is in use then v4a and so on will be used. This can be seen in the output of the command:
ipadm show-addr
If we would like a static address then we can use the syntax
ipadm create-addr -T static -a 192.168.40.3 net0