Oracle Solaris 11 has made a great step forward from version 10, one of those steps was the IPS software packaging system. Many administration tasks are simplified including the ability to verify that the installed contents of a software package match the data that should be installed from the records in the database. In this tutorial we look at using the pkg command and sub-commands search, list, info, contents, verify and fix
Search for packages
No longer do we have to specify the location of a package before we install it. We can now search publishers within configured repositories. A publisher simply refers software that is made available in the repository which is a collections of packages from one or more publishers. Be default Oracle Solaris includes the packages within the solaris publisher in a public http repository. If we are unsure of the name of the package we want to install or manage we can use the pkg command with the search sub-command
pkg search ntp
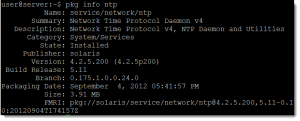
The full name or FMRI of the package is pkg:/service/network/ntp@4.2.5.200-0.175.1.0.0.24.0 but van be referenced in the simplest form of ntp.
Investigate the installed state
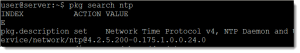
To see if a package is installed we use the list sub-command
pkg list ntp
We can see in the end column the status of I for installed. This could be
- i: Installed
- f: Frozen : package can’t be updated
- o: obsoleted : package won’t be updated.
Gaining information about the package
Using the info sub-command we can print information relating to the package
pkg info ntp
Listing the contents of the package
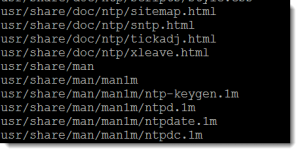
The contents sub-command can be used to list the individual contents of a package
pkg contents ntp
Verify
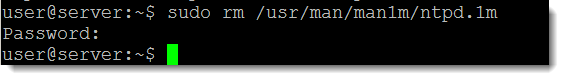
We can verify the package contents that are installed against what should be installed from the package manifest. This is managed by the sub-command verify. First we will delete one of the files from the package, we will need rights to do this so we will use sudo:
sudo rm /usr/man/man1m/ntpd.1m
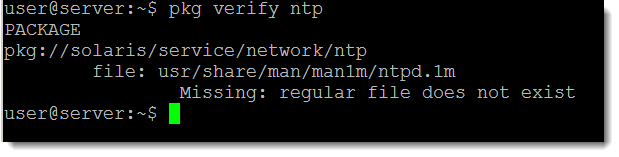
Now when we try to verify the ntp package
pkg verify ntp
We can see from the output that the file we deleted is missing and verify reports an error.
Fixing packages
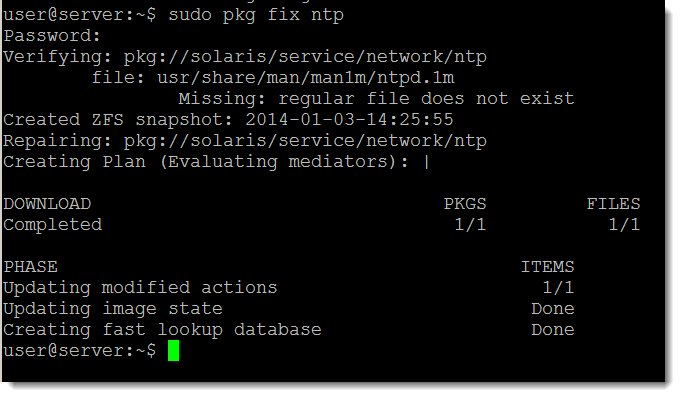
If a package is missing files are they are corrupted in some way we can use the fix sub-command to repair the package.
sudo pkg fix ntp
The package then is located from the repository and the repair carried out. A snapshot is created should you need to roll back the action.