For many years bridging was a topic mainly for networking theory classes. With the rising popularity of virtualization technologies such as XEN and KVM, bridging is back as a mainstream topic. In this tutorial, we will be creating a network bridge interface and connecting to the outside world through the physical eth0 NIC. Other bridges can be connected that do not connect to the physical NIC and can be used for host-only networking. We will be working from the command line on our Ubuntu 12.04 server.
For many years bridging was a topic mainly for networking theory classes. With the rising popularity of virtualization technologies such as XEN and KVM, bridging is back as a mainstream topic. In this tutorial, we will be creating a network bridge interface and connecting to the outside world through the physical eth0 NIC. Other bridges can be connected that do not connect to the physical NIC and can be used for host-only networking. We will be working from the command line on our Ubuntu 12.04 server.
Network Bridges
A bridge is a layer 2 device that works at the data link layer delivering packets based on the destination MAC address. Bridges can be used to segment network traffic and reduce the collision domain. The devices all competing for the same bandwidth. Even though you may not realise it bridges, are most commonly seen in network switches. Traffic only leaves a particular port on a switch if the destination MAC address is available on that port. This differs from the older Hub that sent traffic out on each port of the hub regardless of the data-link address.
Hypervisors
With the advent of virtualisation, we often need to create software bridge interfaces to connect Virtual Machines to the outside world. Software bridges can also be created to allow Virtual Machines to talk with each other but not connect to the outside world. In this tutorial, we will create a bridge in Ubuntu Linux that is connected to the physical eth0 NIC.
Install bridge-utils
The package bridge-utils will need to be installed if we would like our host to be able to bridge traffic. This may save us time later as hypervisors often have this as a prerequisite package.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install bridge-utils
With the package installed we can display currently configured bridges, of course, there are none; with
sudo brctl show
Creating the Bridge
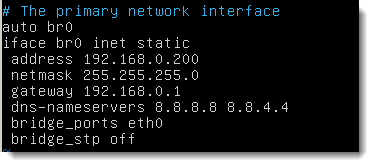
By editing the file, /etc/network/interfaces, we can change references to the interface eth0 to br0. We add the bridge parameters to bridge through eth0, the physical interface and to disable the Spanning Tree Protocol.
auto br0 iface br0 inet static address 192.168.0.201 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.0.1 dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 bridge_ports eth0 bridge_stp off
With this edited and in place, we can restart networking service.
sudo /etc/init.d/network restart
Interface br0
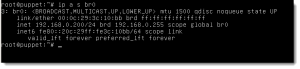
The configured interface now is br0 and no longer eth0. We can see this with the output of :
ip address show br0
We also have the bridge configured now and this will show with the command
brctl show
Summary
We have configured a simple bridge in Ubuntu Server 12.04 that can be used to connect virtual machines to the outside world. In later tutorials, we will look at creating Virtual Machines using KVM.